Common Summertime Sicknesses in Children


Kids’ budding immune systems make them more susceptible to infections than adults, especially when the heat and humidity during summer create a breeding ground for bacteria and viruses to thrive, making it easier for children to catch infectious diseases, such as gastrointestinal infections, hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD), molluscum contagiosum and pink eye. It’s important to know more about these common summer illnesses in kids to keep them healthy.
The 4 most common summer infectious diseases in children:
Enterovirus infection
Enterovirus infection is a kind of gastrointestinal infection that leads to a range of mild to severe illnesses. Most types of enteroviruses are spread through the infected person's gastrointestinal tract (oral, faecal, or food contamination) or respiratory tract (coughing, droplets, or sneezing).
There are dozens of types of enteroviruses, such as poliovirus, coxsackievirus and echovirus, each with its own unique set of symptoms. Infected patients will develop symptoms within one week, including runny nose, headache, fever, red rashes, cough, sore throat, recurrent vomiting, muscle soreness and lethargy. There is currently no specific antiviral medication or vaccine for enteroviruses.
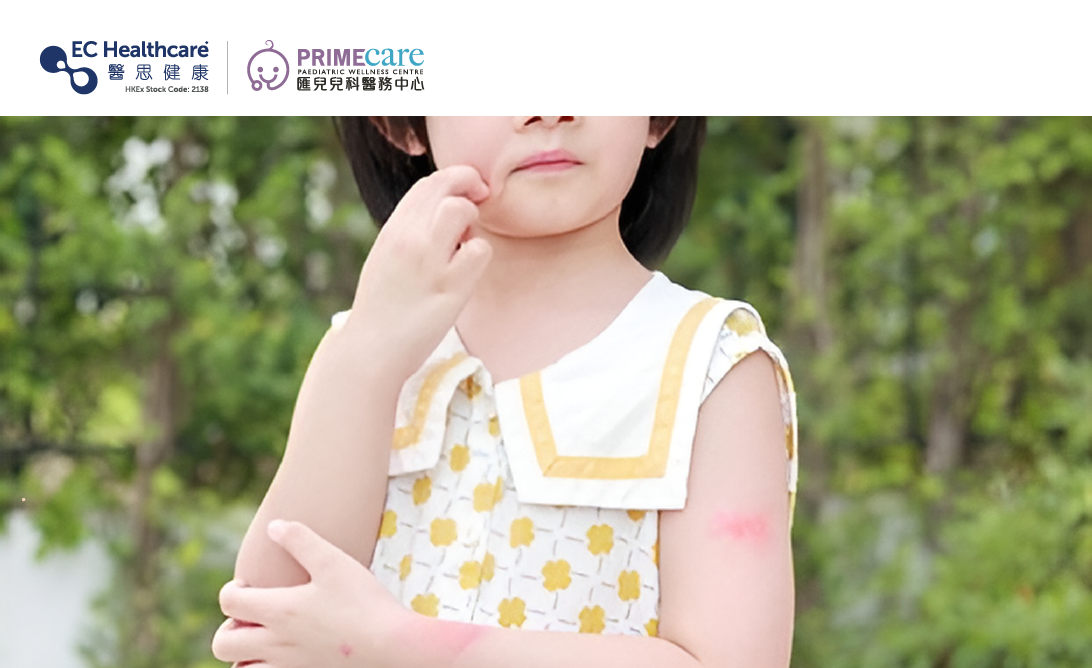
Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD)
HFMD is a contagious infection usually caused by enterovirus 71 and is common in children under 5 years old. Symptoms include fever, oral pain, loss of appetite, low-grade fever, and small blisters or ulcers on the hands, feet, and in the mouth. Most patients recover within a week, but in rare cases, it can lead to complications such as myocarditis, pulmonary oedema and aseptic meningitis. Currently, there is no specific medication to treat hand, foot, and mouth disease. Patients should drink plenty of water, get adequate rest, and use medication to relieve the pain caused by fever and mouth ulcers.
Molluscum contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum, also known as water warts, is a skin infection caused by a poxvirus. It usually affects children aged under 10 as their immune system has not fully developed. Children with eczema and patients with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to molluscum contagiosum and may develop a greater number of lesions and a wider affected area.
Molluscum contagiosum can spread through direct skin-to-skin contact or indirect contact with contaminated objects, such as sharing toys. It can also spread through scratching with infected fingers, which can cause rows of lesions on the skin.
For children with normal immune systems, their lesions will go away in 2 months; only a few cases may persist for 3-5 years.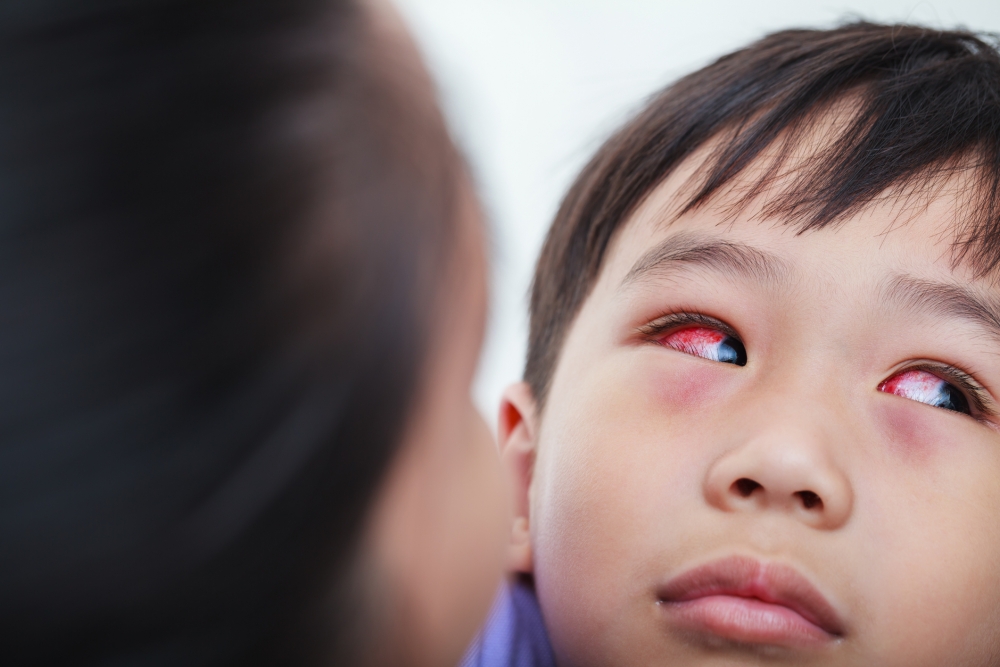
Pink eye
Pink eye, also known as acute infectious conjunctivitis, is an inflammation of the conjunctiva caused by bacteria or viruses. The most common infections are viral conjunctivitis caused by adenoviruses, while bacterial conjunctivitis is less common. Common symptoms of pink eye include tearing, foreign body sensation, itchiness, pain, swelling and redness of the eyes, matted eyelids after sleep, and sensitivity to light.
Pink eye is highly infectious and can easily be transmitted to others. It can spread through direct contact with the discharge from the infected person's eyes or respiratory tracts, or by touching contaminated fingers, clothing, and other objects, including shared eye makeup applicators, towels and topical eye medications.
To keep infectious diseases at bay in our beloved children, parents can teach them some preventive measures:
-Maintain good personal hygiene
-Wash your hands thoroughly and regularly, and rub them with liquid soap for at least 20 seconds
-Do not consume contaminated food or water
-Do not share personal items
-Avoid intimate contact with patients
-Avoid eating uncooked food
If your children get infectious diseases unfortunately, take personal protective measures and seek medical attention immediately. Early treatment can help prevent complications and facilitate a speedy recovery. To prevent spreading the virus, infected children should avoid going to school, swimming, or participating in group activities until they have fully recovered. If your child is feeling unwell, bring them to a doctor as soon as possible.










